THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
The musculoskeletal system
In the musculoskeletal system, the muscular and skeletal systems work together to support and move the body.
The bones of the skeletal system serve to protect the body's organs, support the weight of the body, and give the body shape. The muscles of the muscular system attach to these bones, pulling on them to allow for movement of the body.
The human skeleton
The human skeleton performs several major functions.
It protects the internal organs, supports and gives shape to the body and allows for movement. It also is the site of blood cell production, which occurs in the marrow of some bones.
The skeleton
The human skeleton is divided into two parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
The axial skeleton consists of:
- the skull, which protects the brain and supports facial structure
- the vertebral column (spine), which surrounds and protects the spinal cord and support the head
- the thoracic (rib) cage, which surrounds and protects the organs within the chest (including heart and lungs)
The appendicular skeleton consists of:
- the pectoral girdle (shoulders):
- upper and lower limbs (arms and legs)
- the pelvic girdle (hip bones) and lower limbs (legs)
The musculoskeletal system also contains connective structures and tissues that support the body and allow for its movement:
*Cartilage acts as a shock absorber to reduce friction.
*Ligaments help stabilize the joint, keeping it from moving outside of its intended range of motion.
*Tendons connect the skeletal system to the muscular system by attaching muscle to bone. When muscle contracts, the tendon acts on the bone, causing movement.
*Joints, the point at which two or more bones connect, can be fixed, slightly movable, or freely movable.
Muscles
The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
*Skeletal muscle is voluntary and striated. These are the muscles that attach to bones and control conscious movement.
*Smooth muscle is involuntary and non-striated. It is found in the hollow organs of the body, such as the stomach, intestines, and around blood vessels.
* Cardiac muscle is involuntary and striated. It is found only in the heart and is specialized to help pump blood throughout the body.
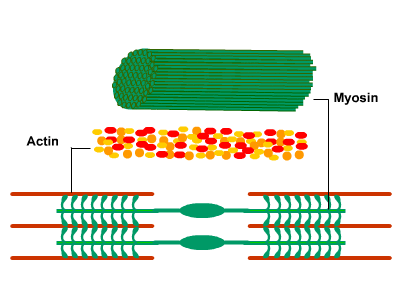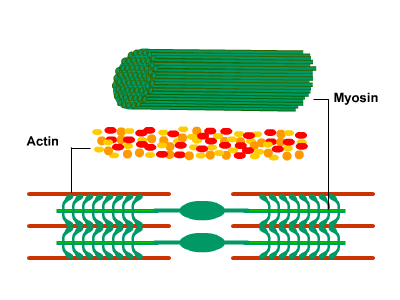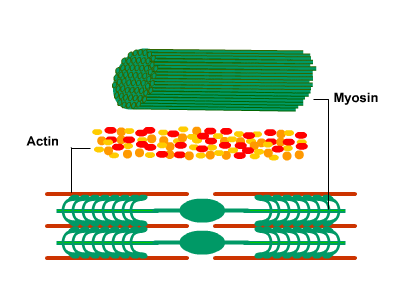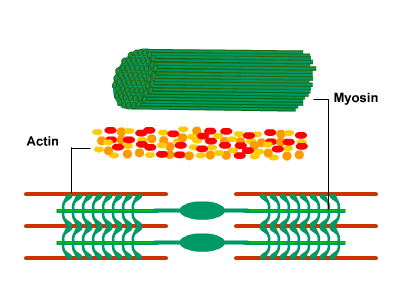
Muscle contraction
When a muscle fiber receives a signal from the nervous system, myosin filaments are stimulated, pulling actin filaments closer together. This shortens sarcomeres within a fiber, causing it to contract.
*Cross bridge cycle: it's the responsable of the muscle movement
- The actin-myosin bridge very rapidly dissociates due to ATP binding to myosin.
- The free myosin bridge moves into position to attach to actin, during which ATP is hydrolyzed.
- The free myosin bridge along with its hydrolysis products rebinds to the actin filament.
- The cross-bridge generates force, and actin displaces the reaction products (ADP and Pi) from the myosin cross-bridge. This is the rate-limiting step of contraction. The actin-myosin cross-bridge is now ready for the ATP binding of step 1.


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario